
TORRANCE, CA, May 28, 2025 – Navitas Semiconductor is collaborating with NVIDIA to support its next-generation 800 V HVDC architecture. This collaboration focuses on integrating Navitas’ GaNFast and GeneSiC power devices into NVIDIA’s ‘Kyber’ rack-scale systems, which are designed to deliver power for GPUs like the Rubin Ultra. GaN and SiC technologies enhance efficiency and performance in dense computing setups.
NVIDIA’s 800V DC architecture is developed to provide scalable and efficient power delivery for AI systems, with the goal of streamlining infrastructure requirements.
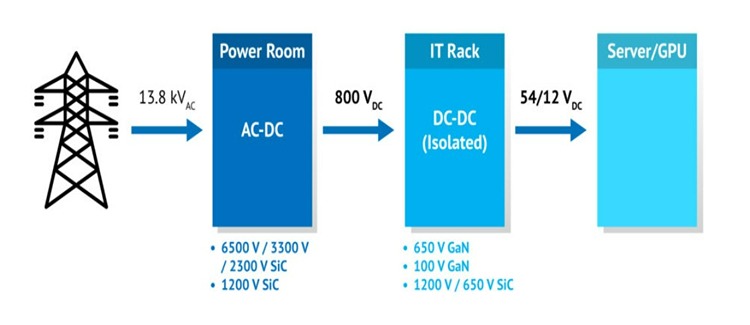
Most data centers today use a standard 54 V in-rack power setup, supporting only a few hundred kilowatts (kW). Bulky copper busbars carry the low-voltage power from the rack-mounted power shelves to the compute trays. At power levels above 200 kW, the architecture faces constraints from power density, copper usage, and lower efficiency.
Modern AI data centers require gigawatts (GW) of power for the increasing demand for AI computation. NVIDIA’s approach is to convert the 13.8 kV AC grid power to 800 V HVDC at the data center perimeter using solid state transformers (SST) and industrial-grade rectifiers, eliminating AC/DC and DC/DC conversion steps.
Due to the higher voltage level of 800 V HVDC, the thickness of copper wires can be reduced by up to 45%, due to I2R losses, where the same amount of power can be delivered with increased voltage and lower current. Using a traditional 54V DC system, over 200 kg of copper would be needed to power a 1MW rack, which is not sustainable for next-generation AI data centers with GW power demand.
The 800V HVDC supplies power directly to IT racks, removing the need for separate AC-DC conversion. DC-DC converters then step down the voltage to levels required by GPUs like the Rubin Ultra.
Navitas develops GaN and SiC-based solutions for AI data center applications. Its GaNSafe power ICs combine control, drive, sensing, and protection features to support operational reliability. The devices include short-circuit protection with a 350 ns response time, 2kV ESD protection on all pins, removal of negative gate drive, and adjustable slew rate control. These features are managed through a 4-pin interface, allowing the device to function similarly to a discrete GaN FET without requiring a VCC pin. All these features are controlled with 4-pins, allowing the package to be treated like a discrete GaN FET.
Navitas also provides 80-120V GaN devices optimized for secondary-side DC-DC conversion in AI data center PSUs, supporting 48V–54V outputs with high speed, efficiency, and compact size.
Enabled by 20 years of SiC innovation leadership, GeneSiC proprietary ‘trench-assisted planar’ technology offers stable operation across temperature ranges, supporting prompt switching and effective thermal management for high-power, high-reliability use cases. G3F SiC MOSFETs support fast-switching operation, with up to 25°C lower case temperatures and potentially longer operational life compared to standard SiC devices.
Offering the industry’s voltage range – stretching from 650 V to 2.3 kV to 6.5 kV, the SiC technology has been implemented in multiple projects for MW energy storage and grid-tied inverters with the Department of Energy (DoE).
In August 2023, Navitas introduced 3.2 kW CRPS, achieving a 40% smaller size than best-in-class, legacy silicon solutions for AI and Edge computing. It was followed by the world’s highest power density 4.5 kW CRPS, achieving 137 W/in3, and an efficiency of over 97%. In November 2024, Navitas released the world’s first 8.5 kW AI data center power supply, powered by GaN and SiC that could meet 98% efficiency, complying with the Open Compute Project (OCP) and Open Rack v3 (ORv3) specifications. Additionally, Navitas created IntelliWeave, an innovative patented new digital control technique, that when combined with GaNSafe and Gen 3-Fast SiC MOSFETs, enables PFC peak efficiencies to 99.3% and reduces power losses by 30% compared to existing solutions. Alongside the Computex exhibition in Taiwan, the newest release of their 12 kW PSU was presented at the Navitas ‘AI Tech Night’ on May 21, 2025.
“We are proud to be selected by NVIDIA to collaborate on their 800 HVDC architecture initiative. Our latest innovations in high-power GaN and SiC technologies have seen world firsts and have created new inflections into markets such as AI datacenters and electric vehicles”, said Gene Sheridan, CEO and co-founder of Navitas. “With our wide portfolio range, we can support NVIDIA’s 800V HVDC infrastructure, from grid to the GPU. We appreciate that NVIDIA recognizes our technology and commitment to driving the next generation of data center power delivery.”
Source: Navitas
About Navitas

Navitas Semiconductor, founded in 2014 and headquartered in Torrance, CA, designs and manufactures power semiconductors based on gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) technologies. Operating under the GaNFast and GeneSiC brands, the company develops integrated GaN power ICs and SiC devices for use in applications such as AI data centers, electric vehicles, renewable energy, energy storage, industrial systems, and consumer electronics. In 2024, Navitas reported annual revenue of $83.3 million. The company employs approximately 280 people. GaNFast ICs combine power switching with control, sensing, and protection features, while GeneSiC devices target high-voltage and high-reliability applications. Navitas holds over 300 issued or pending patents and offers a 20-year warranty on its GaNFast products. It is also recognized as the first semiconductor company to achieve CarbonNeutral certification.
About NVIDIA
![]()
NVIDIA Corporation, based in Santa Clara, CA, is a U.S. technology company specializing in the design and production of graphics processing units (GPUs). It’s hardware and software solutions support a range of applications and simulation. Operating for over 30 years, NVIDIA has seen strong financial growth, reporting $39.3 billion in revenue and $22.1 billion in net income for the fiscal quarter ending January 2025. Its headquarters are designed to promote a flat organizational structure that encourages open communication and collaboration between leadership and staff across industries. In gaming, its GPUs power high-performance visual rendering. In AI and high-performance computing, NVIDIA provides the infrastructure needed for training and deploying large-scale models. The company also contributes to the automotive sector with systems for autonomous driving and supports robotics with tools for AI-based perception.
